Heel Pain All It Is Best To Know Heel Soreness
Overview

Heel pain is usually felt either under the heel or just behind it. Heel Pain has a prevalence of 3.6%. US studies estimate that 7% of older adults report tenderness under the heel. Plantar fasciitis is estimated to account for 8% of all running-related injuries. There are 26 bones in the human foot, of which the heel is the largest. Pain typically comes on gradually, with no injury to the affected area. It is often triggered by wearing a flat shoe. In most cases the pain is under the foot, towards the front of the heel. The majority of patients recover with conservative treatments within months. Home care such as rest, ice, proper-fitting footwear and foot supports are often enough to ease heel pain. To prevent heel pain, it's recommended to reduce the stress on that part of the body.
Causes
The most common cause of heel pain in adults is plantar fasciitis, which is an inflammation of the band of tissue in the sole that connects the heel to the toes and forms the natural foot arch. Plantar fasciitis may or may not be complicated by a calcaneal spur, a small bone growth that protrudes out of the heel. Plantar fasciitis may also be referred to as plantar fasciosis. In contrast to fasciitis, which essentially means inflammation, fasciosis refers to degeneration of the tissue. In fact, if left untreated, acute plantar fasciitis may develop into a chronic painful condition, which results in slow and irreversible degeneration of the fascia, hence plantar fasciosis. The location of the pain is usually exactly under the heel but may also occur in the arch of the foot. Pain typical to plantar fasciitis is that which feels worse when arising on to your feet such as in mornings or after sitting down for a while, and usually progresses in severity when left untreated.
Symptoms
Symptoms may also include swelling that is quite tender to the touch. Standing, walking and constrictive shoe wear typically aggravate symptoms. Many patients with this problem are middle-aged and may be slightly overweight. Another group of patients who suffer from this condition are young, active runners.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of heel pain generally occurs in stages. At the earliest sign of heel pain, aggressive calf muscle stretching should be started. Additionally, taking an oral anti-inflammatory medication and over-the- counter arch supports or heel cushions may be beneficial. The next phase of treatment might consist of continued calf muscle stretching exercises, cortisone injections and orthopedic taping of the foot to support the arch. If this treatment fails, or if there is reoccurrence of the heel pain, then functional foot orthotics might be considered. A functional orthotic is a device that is prescribed and fitted by your foot doctor, which fits in normal shoes like an arch support. Unlike an arch support, however the orthotic corrects abnormal pronation of the subtalar joint. Thus orthotics address the cause of the heel pain - abnormal pronation of the foot. Pump bump, treatment is similar to the treatment of bursitis and heel spurs. In rare cases, the bony growth at the heel may need to be removed surgically. Heel bruises can be treated by applying an ice pack for the first few minutes after injury. Achilles tendonitis, this condition is treated conservatively with rest, NSAIDs and physical therapy. If a sprain, fracture or other injury has caused the trapped nerve, this underlying problem must be treated first. In rare cases, surgery may be done to release the trapped nerve.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is a last resort in the treatment of heel pain. Physicians have developed many procedures in the last 100 years to try to cure heel pain. Most procedures that are commonly used today focus on several areas, remove the bone spur (if one is present), release the plantar fascia (plantar fasciotomy), release pressure on the small nerves in the area. Usually the procedure is done through a small incision on the inside edge of the foot, although some surgeons now perform this type of surgery using an endoscope. An endoscope is a tiny TV camera that can be inserted into a joint or under the skin to allow the surgeon to see the structures involved in the surgery. By using the endoscope, a surgeon can complete the surgery with a smaller incision and presumably less damage to normal tissues. It is unclear whether an endoscopic procedure for this condition is better than the traditional small incision. Surgery usually involves identifying the area where the plantar fascia attaches to the heel and releasing the fascia partially from the bone. If a small spur is present this is removed. The small nerves that travel under the plantar fascia are identified and released from anything that seems to be causing pressure on the nerves. This surgery can usually be done on an outpatient basis. This means you can leave the hospital the same day.
Prevention

Make sure you wear appropriate supportive shoes. Don't over-train in sports. Make sure you warm up, cool down and undertake an exercise regime that helps maintain flexibility. Manage your weight, obesity is a factor in causing plantar fasciitis. Avoid walking and running on hard surfaces if you are prone to pain. You should follow the recognized management protocol "RICED" rest, ice, compression, elevation and diagnosis. Rest, keep off the injured ankle as much as possible. Ice, applied for 20 minutes at a time every hour as long as swelling persists. Compression, support the ankle and foot with a firmly (not tightly) wrapped elastic bandage. Elevation, keep foot above heart level to minimize bruising and swelling. Diagnosis. Consult a medical professional (such as a Podiatrist or doctor) especially if you are worried about the injury, or if the pain or swelling gets worse. If the pain or swelling has not gone down significantly within 48 hours, also seek treatment. An accurate diagnosis is essential for proper rehabilitation of moderate to severe injuries.

Heel pain is usually felt either under the heel or just behind it. Heel Pain has a prevalence of 3.6%. US studies estimate that 7% of older adults report tenderness under the heel. Plantar fasciitis is estimated to account for 8% of all running-related injuries. There are 26 bones in the human foot, of which the heel is the largest. Pain typically comes on gradually, with no injury to the affected area. It is often triggered by wearing a flat shoe. In most cases the pain is under the foot, towards the front of the heel. The majority of patients recover with conservative treatments within months. Home care such as rest, ice, proper-fitting footwear and foot supports are often enough to ease heel pain. To prevent heel pain, it's recommended to reduce the stress on that part of the body.
Causes
The most common cause of heel pain in adults is plantar fasciitis, which is an inflammation of the band of tissue in the sole that connects the heel to the toes and forms the natural foot arch. Plantar fasciitis may or may not be complicated by a calcaneal spur, a small bone growth that protrudes out of the heel. Plantar fasciitis may also be referred to as plantar fasciosis. In contrast to fasciitis, which essentially means inflammation, fasciosis refers to degeneration of the tissue. In fact, if left untreated, acute plantar fasciitis may develop into a chronic painful condition, which results in slow and irreversible degeneration of the fascia, hence plantar fasciosis. The location of the pain is usually exactly under the heel but may also occur in the arch of the foot. Pain typical to plantar fasciitis is that which feels worse when arising on to your feet such as in mornings or after sitting down for a while, and usually progresses in severity when left untreated.
Symptoms
Symptoms may also include swelling that is quite tender to the touch. Standing, walking and constrictive shoe wear typically aggravate symptoms. Many patients with this problem are middle-aged and may be slightly overweight. Another group of patients who suffer from this condition are young, active runners.
Diagnosis
A biomechanical exam by your podiatrist will help reveal these abnormalities and in turn resolve the cause of plantar fasciitis. By addressing this cause, the patient can be offered a podiatric long-term solution to his problem.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of heel pain generally occurs in stages. At the earliest sign of heel pain, aggressive calf muscle stretching should be started. Additionally, taking an oral anti-inflammatory medication and over-the- counter arch supports or heel cushions may be beneficial. The next phase of treatment might consist of continued calf muscle stretching exercises, cortisone injections and orthopedic taping of the foot to support the arch. If this treatment fails, or if there is reoccurrence of the heel pain, then functional foot orthotics might be considered. A functional orthotic is a device that is prescribed and fitted by your foot doctor, which fits in normal shoes like an arch support. Unlike an arch support, however the orthotic corrects abnormal pronation of the subtalar joint. Thus orthotics address the cause of the heel pain - abnormal pronation of the foot. Pump bump, treatment is similar to the treatment of bursitis and heel spurs. In rare cases, the bony growth at the heel may need to be removed surgically. Heel bruises can be treated by applying an ice pack for the first few minutes after injury. Achilles tendonitis, this condition is treated conservatively with rest, NSAIDs and physical therapy. If a sprain, fracture or other injury has caused the trapped nerve, this underlying problem must be treated first. In rare cases, surgery may be done to release the trapped nerve.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is a last resort in the treatment of heel pain. Physicians have developed many procedures in the last 100 years to try to cure heel pain. Most procedures that are commonly used today focus on several areas, remove the bone spur (if one is present), release the plantar fascia (plantar fasciotomy), release pressure on the small nerves in the area. Usually the procedure is done through a small incision on the inside edge of the foot, although some surgeons now perform this type of surgery using an endoscope. An endoscope is a tiny TV camera that can be inserted into a joint or under the skin to allow the surgeon to see the structures involved in the surgery. By using the endoscope, a surgeon can complete the surgery with a smaller incision and presumably less damage to normal tissues. It is unclear whether an endoscopic procedure for this condition is better than the traditional small incision. Surgery usually involves identifying the area where the plantar fascia attaches to the heel and releasing the fascia partially from the bone. If a small spur is present this is removed. The small nerves that travel under the plantar fascia are identified and released from anything that seems to be causing pressure on the nerves. This surgery can usually be done on an outpatient basis. This means you can leave the hospital the same day.
Prevention

Make sure you wear appropriate supportive shoes. Don't over-train in sports. Make sure you warm up, cool down and undertake an exercise regime that helps maintain flexibility. Manage your weight, obesity is a factor in causing plantar fasciitis. Avoid walking and running on hard surfaces if you are prone to pain. You should follow the recognized management protocol "RICED" rest, ice, compression, elevation and diagnosis. Rest, keep off the injured ankle as much as possible. Ice, applied for 20 minutes at a time every hour as long as swelling persists. Compression, support the ankle and foot with a firmly (not tightly) wrapped elastic bandage. Elevation, keep foot above heart level to minimize bruising and swelling. Diagnosis. Consult a medical professional (such as a Podiatrist or doctor) especially if you are worried about the injury, or if the pain or swelling gets worse. If the pain or swelling has not gone down significantly within 48 hours, also seek treatment. An accurate diagnosis is essential for proper rehabilitation of moderate to severe injuries.
What Are The Key Treatment And Cause Of Achilles Tendon Pain ?
Overview
 If you have pain along the back of your leg near your heel, you may have Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that commonly occurs in runners and ?weekend warriors?. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. Named after a tragic hero from Greek mythology, it connects your calf muscle to your heel bone to allow you to jump, run and walk. Achilles tendonitis is most common in middle-aged men, but it can happen to anyone who has a sudden increase in physical activity. The risk is increased if you also have tight calf muscles and/or a flat arch in your foot. Other risk factors include running in worn out shoes, cold weather, frequently running uphill or if you suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis is when the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon have started to break down with tiny tears, swell, and/or thicken. This type is more often seen in younger, active people. Both types can also cause bone spurs. Achilles tendonitis should be diagnosed by your doctor. However, if you experienced a sudden ?pop? in the back of your calf or heel, this might be something more serious like a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon. If this happens, see your doctor immediately.
If you have pain along the back of your leg near your heel, you may have Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that commonly occurs in runners and ?weekend warriors?. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. Named after a tragic hero from Greek mythology, it connects your calf muscle to your heel bone to allow you to jump, run and walk. Achilles tendonitis is most common in middle-aged men, but it can happen to anyone who has a sudden increase in physical activity. The risk is increased if you also have tight calf muscles and/or a flat arch in your foot. Other risk factors include running in worn out shoes, cold weather, frequently running uphill or if you suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis is when the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon have started to break down with tiny tears, swell, and/or thicken. This type is more often seen in younger, active people. Both types can also cause bone spurs. Achilles tendonitis should be diagnosed by your doctor. However, if you experienced a sudden ?pop? in the back of your calf or heel, this might be something more serious like a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon. If this happens, see your doctor immediately.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis include, overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions, both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with flat feet or hyperpronated feet (feet that turn inward while walking) are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon. Quinolone antibiotics - can in some instances be associated with inflammatory tenosynovitis and, if present, will often be bilateral (both Achilles), coming on soon after exposure to the drug.
Symptoms
Achilles tendonitis and tendinopathy present as pain in the Achilles tendon, usually several centimeters above where it inserts on the heel. In some patients, pain and tendon damage are primarily at the insertion to the heel bone. There may be swelling and/or thickening of the tendon. Bending at the ankle, walking, jumping, and running are often painful with this condition.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist can usually make the diagnosis by clinical history and physical examination alone. Pain with touching or stretching the tendon is typical. There may also be a visible swelling to the tendon. The patient frequently has difficulty plantarflexing (pushing down the ball of the foot and toes, like one would press on a gas pedal), particularly against resistance. In most cases X-rays don't show much, as they tend to show bone more than soft tissues. But X-rays may show associated degeneration of the heel bone that is common with Achilles Tendon problems. For example, heel spurs, calcification within the tendon, avulsion fractures, periostitis (a bruising of the outer covering of the bone) may all be seen on X-ray. In cases where we are uncertain as to the extent of the damage to the tendon, though, an MRI scan may be necessary, which images the soft tissues better than X-rays. When the tendon is simply inflamed and not severely damaged, the problem may or may not be visible on MRI. It depends upon the severity of the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Initial treatment of mild Achilles tendinitis involves rest, stretching exercises, and non-prescriptive medications to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. These medications include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Relief of pain and swelling may be achieved with the application of ice for15 minutes at a time. Sleeping with the affected foot propped up on a pillow may also relieve swelling. Adequate time must be given to rest and recovery, meaning months or weeks, to prevent re-injury of the Achilles tendon. Most people make a full recovery and are able to return to their regular sports and exercise programs.

Surgical Treatment
Percutaneous Achilles Tendon Surgery. During this procedure the surgeon will make 3 to 4 incisions (approx. 2.5 cm long) on both sides of the Achilles tendon. Small forceps are used to free the tendon sheath (the soft tissue casing around your Achilles tendon) to make room for the surgeon to stitch/suture any tears. Skilled surgeons may perform a percutaneous achilles tendon surgery with ultrasound imaging techniques to allow for blink suturing with stab incisions made by a surgical suture needle. This procedure can be done in 3 different ways depending on the preference and experience of your surgeon. Instead of making several 2.5 cm incisions for this procedure, some surgeons will use guided imaging with an ultrasound to see the Achilles tendon tissue without having to open up your ankle. For this technique, they will use a surgical needle to repeatedly stab your Achilles tendon. These "stab incisions" will allow the surgeon to "blindly" suture your tendon without seeing the actual tissue. As another option - some surgeons will only make 1 to 3 incisions for smaller surgical implements to repair your tendon while relying on imaging ultrasound to see your damaged tissue. During either procedure the use of ultrasound imaging or endoscopic techniques requires a very skilled surgeon.
Prevention
By properly training the body, an athlete can build the strength of their tendons and muscles. Following a workout and dieting plan, the body will be able to build muscle and strengthen most effectively. Additionally, doing the following can prevent tendinitis. Wearing appropriate shoes will give your foot the support it needs for proper movements of the foot and ankle. Improper movements will put additional stress on your body. Stretching before an athletic activity, Stretching primes the body for a taxing activity. Additionally, this will get your blood flowing and reduce the risk of pulling a muscle. Ask your doctor about orthotics, Custom orthotics can help get your foot into proper alignment. If the foot does not execute proper mechanics, the body will adjust which will cause pain and increase the chances of injury.
 If you have pain along the back of your leg near your heel, you may have Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that commonly occurs in runners and ?weekend warriors?. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. Named after a tragic hero from Greek mythology, it connects your calf muscle to your heel bone to allow you to jump, run and walk. Achilles tendonitis is most common in middle-aged men, but it can happen to anyone who has a sudden increase in physical activity. The risk is increased if you also have tight calf muscles and/or a flat arch in your foot. Other risk factors include running in worn out shoes, cold weather, frequently running uphill or if you suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis is when the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon have started to break down with tiny tears, swell, and/or thicken. This type is more often seen in younger, active people. Both types can also cause bone spurs. Achilles tendonitis should be diagnosed by your doctor. However, if you experienced a sudden ?pop? in the back of your calf or heel, this might be something more serious like a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon. If this happens, see your doctor immediately.
If you have pain along the back of your leg near your heel, you may have Achilles tendonitis. Achilles tendonitis is an overuse injury that commonly occurs in runners and ?weekend warriors?. The Achilles tendon is the largest tendon in the body. Named after a tragic hero from Greek mythology, it connects your calf muscle to your heel bone to allow you to jump, run and walk. Achilles tendonitis is most common in middle-aged men, but it can happen to anyone who has a sudden increase in physical activity. The risk is increased if you also have tight calf muscles and/or a flat arch in your foot. Other risk factors include running in worn out shoes, cold weather, frequently running uphill or if you suffer from medical conditions such as diabetes or high blood pressure. There are two main types of Achilles tendinitis: insertional and noninsertional. Insertional Achilles tendinitis involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. Noninsertional Achilles tendinitis is when the fibers in the middle portion of the tendon have started to break down with tiny tears, swell, and/or thicken. This type is more often seen in younger, active people. Both types can also cause bone spurs. Achilles tendonitis should be diagnosed by your doctor. However, if you experienced a sudden ?pop? in the back of your calf or heel, this might be something more serious like a ruptured or torn Achilles tendon. If this happens, see your doctor immediately.
Causes
Some of the causes of Achilles tendonitis include, overuse injury - this occurs when the Achilles tendon is stressed until it develops small tears. Runners seem to be the most susceptible. People who play sports that involve jumping, such as basketball, are also at increased risk. Arthritis - Achilles tendonitis can be a part of generalised inflammatory arthritis, such as ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis. In these conditions, both tendons can be affected. Foot problems - some people with flat feet or hyperpronated feet (feet that turn inward while walking) are prone to Achilles tendonitis. The flattened arch pulls on calf muscles and keeps the Achilles tendon under tight strain. This constant mechanical stress on the heel and tendon can cause inflammation, pain and swelling of the tendon. Being overweight can make the problem worse. Footwear - wearing shoes with minimal support while walking or running can increase the risk, as can wearing high heels. Overweight and obesity - being overweight places more strain on many parts of the body, including the Achilles tendon. Quinolone antibiotics - can in some instances be associated with inflammatory tenosynovitis and, if present, will often be bilateral (both Achilles), coming on soon after exposure to the drug.
Symptoms
Achilles tendonitis and tendinopathy present as pain in the Achilles tendon, usually several centimeters above where it inserts on the heel. In some patients, pain and tendon damage are primarily at the insertion to the heel bone. There may be swelling and/or thickening of the tendon. Bending at the ankle, walking, jumping, and running are often painful with this condition.
Diagnosis
A podiatrist can usually make the diagnosis by clinical history and physical examination alone. Pain with touching or stretching the tendon is typical. There may also be a visible swelling to the tendon. The patient frequently has difficulty plantarflexing (pushing down the ball of the foot and toes, like one would press on a gas pedal), particularly against resistance. In most cases X-rays don't show much, as they tend to show bone more than soft tissues. But X-rays may show associated degeneration of the heel bone that is common with Achilles Tendon problems. For example, heel spurs, calcification within the tendon, avulsion fractures, periostitis (a bruising of the outer covering of the bone) may all be seen on X-ray. In cases where we are uncertain as to the extent of the damage to the tendon, though, an MRI scan may be necessary, which images the soft tissues better than X-rays. When the tendon is simply inflamed and not severely damaged, the problem may or may not be visible on MRI. It depends upon the severity of the condition.
Nonsurgical Treatment
Initial treatment of mild Achilles tendinitis involves rest, stretching exercises, and non-prescriptive medications to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. These medications include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) such as ibuprofen or naproxen. Relief of pain and swelling may be achieved with the application of ice for15 minutes at a time. Sleeping with the affected foot propped up on a pillow may also relieve swelling. Adequate time must be given to rest and recovery, meaning months or weeks, to prevent re-injury of the Achilles tendon. Most people make a full recovery and are able to return to their regular sports and exercise programs.

Surgical Treatment
Percutaneous Achilles Tendon Surgery. During this procedure the surgeon will make 3 to 4 incisions (approx. 2.5 cm long) on both sides of the Achilles tendon. Small forceps are used to free the tendon sheath (the soft tissue casing around your Achilles tendon) to make room for the surgeon to stitch/suture any tears. Skilled surgeons may perform a percutaneous achilles tendon surgery with ultrasound imaging techniques to allow for blink suturing with stab incisions made by a surgical suture needle. This procedure can be done in 3 different ways depending on the preference and experience of your surgeon. Instead of making several 2.5 cm incisions for this procedure, some surgeons will use guided imaging with an ultrasound to see the Achilles tendon tissue without having to open up your ankle. For this technique, they will use a surgical needle to repeatedly stab your Achilles tendon. These "stab incisions" will allow the surgeon to "blindly" suture your tendon without seeing the actual tissue. As another option - some surgeons will only make 1 to 3 incisions for smaller surgical implements to repair your tendon while relying on imaging ultrasound to see your damaged tissue. During either procedure the use of ultrasound imaging or endoscopic techniques requires a very skilled surgeon.
Prevention
By properly training the body, an athlete can build the strength of their tendons and muscles. Following a workout and dieting plan, the body will be able to build muscle and strengthen most effectively. Additionally, doing the following can prevent tendinitis. Wearing appropriate shoes will give your foot the support it needs for proper movements of the foot and ankle. Improper movements will put additional stress on your body. Stretching before an athletic activity, Stretching primes the body for a taxing activity. Additionally, this will get your blood flowing and reduce the risk of pulling a muscle. Ask your doctor about orthotics, Custom orthotics can help get your foot into proper alignment. If the foot does not execute proper mechanics, the body will adjust which will cause pain and increase the chances of injury.
What Triggers Plantar Fasciitis And How To Eliminate It

Overview
A common condition that affects people of all ages. Symptoms include heel pain that is worse upon arising in the morning or standing after prolonged sitting. The pain is caused by inflammation of the plantar fascia, the ligament that connects the heel bone to the toes.
Causes
As a person gets older, the plantar fascia becomes less like a rubber band and more like a rope that doesn't stretch very well. The fat pad on the heel becomes thinner and can't absorb as much of the shock caused by walking. The extra shock damages the plantar fascia and may cause it to swell, tear or bruise. You may notice a bruise or swelling on your heel. Other risk factors for plantar fasciitis include being overweight and obesity. Diabetes. Spending most of the day on your feet. Becoming very active in a short period of time. Being flat-footed or having a high arch.
Symptoms
Symptoms of plantar fasciitis can occur suddenly or gradually. When they occur suddenly, there is usually intense heel pain on taking the first morning steps, known as first-step pain. This heel pain will often subside as you begin to walk around, but it may return in the late afternoon or evening. When symptoms occur gradually, a more long-lasting form of heel pain will cause you to shorten your stride while running or walking. You also may shift your weight toward the front of the foot, away from the heel.
Diagnosis
To diagnose plantar fasciitis, your doctor will physically examine your foot by testing your reflexes, balance, coordination, muscle strength, and muscle tone. Your doctor may also advise a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or X-ray to rule out other others sources of your pain, such as a pinched nerve, stress fracture, or bone spur.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment of plantar fasciitis begins with first-line strategies, which you can begin at home. Stretching exercises. Exercises that stretch out the calf muscles help ease pain and assist with recovery. Avoid going barefoot. When you walk without shoes, you put undue strain and stress on your plantar fascia. Ice. Putting an ice pack on your heel for 20 minutes several times a day helps reduce inflammation. Place a thin towel between the ice and your heel,do not apply ice directly to the skin. Limit activities. Cut down on extended physical activities to give your heel a rest. Shoe modifications. Wearing supportive shoes that have good arch support and a slightly raised heel reduces stress on the plantar fascia. Medications. Oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation. If you still have pain after several weeks, see your foot and ankle surgeon, who may add one or more of these treatment approaches. Padding and strapping. Placing pads in the shoe softens the impact of walking. Strapping helps support the foot and reduce strain on the fascia. Orthotic devices. Custom orthotic devices that fit into your shoe help correct the underlying structural abnormalities causing the plantar fasciitis. Injection therapy. In some cases, corticosteroid injections are used to help reduce the inflammation and relieve pain. Removable walking cast. A removable walking cast may be used to keep your foot immobile for a few weeks to allow it to rest and heal. Night splint. Wearing a night splint allows you to maintain an extended stretch of the plantar fascia while sleeping. This may help reduce the morning pain experienced by some patients. Physical therapy. Exercises and other physical therapy measures may be used to help provide relief.

Surgical Treatment
Most patients have good results from surgery. However, because surgery can result in chronic pain and dissatisfaction, it is recommended only after all nonsurgical measures have been exhausted. The most common complications of release surgery include incomplete relief of pain and nerve damage.
Stretching Exercises
While it's typical to experience pain in just one foot, massage and stretch both feet. Do it first thing in the morning, and three times during the day. Achilles Tendon Stretch. Stand with your affected foot behind your healthy one. Point the toes of the back foot toward the heel of the front foot, and lean into a wall. Bend the front knee and keep the back knee straight, heel firmly planted on the floor. Hold for a count of 10. Plantar Fascia Stretch. Sit down, and place the affected foot across your knee. Using the hand on your affected side, pull your toes back toward your shin until you feel a stretch in your arch. Run your thumb along your foot--you should feel tension. Hold for a count of 10.
What Causes Plantar Fasciitis To Surface
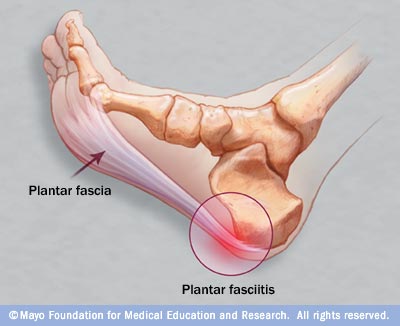
Overview
The plantar fascia (a connective tissue structure) stretches from the toes and ball of the foot, through the arch, and connects to the heel bone in three places: outside, center and inside. Normally it helps the foot spring as it rolls forward. It also provides support for the arch of the foot. The plantar fascia helps keep the foot on track, cutting down on oscillation. When the foot over-pronates (rolls to the inside) the plantar fascia tries to stabilize it and prevent excessive roll. In time, the inside and sometimes center connections are overstressed and pull away from their attachments. The first sign is usually heel pain as you rise in the morning. When you walk around, the pain may subside, only to return the next morning. Inflammation and increased soreness are the results of long-term neglect and continued abuse. A heel bone spur may develop after a long period of injury when there is no support for the heel. The plantar fascia attaches to the heel bone with small fibers. When these become irritated they become inflamed with blood containing white blood cells. Within the white blood cells are osteoblasts which calcify to form bone spurs and calcium deposits. The body is trying to reduce stress on that area by building a bone in the direction of stress. Unfortunately, these foreign substances cause pain and further irritation in the surrounding soft tissue.
Causes
You're more likely to develop the condition if you're female, overweight or have a job that requires a lot of walking or standing on hard surfaces. You're also at risk if you walk or run for exercise, especially if you have tight calf muscles that limit how far you can flex your ankles. People with very flat feet or very high arches also are more prone to plantar fasciitis.
Symptoms
Most people with plantar fasciitis have pain when they take their first steps after they get out of bed or sit for a long time. You may have less stiffness and pain after you take a few steps. But your foot may hurt more as the day goes on. It may hurt the most when you climb stairs or after you stand for a long time. If you have foot pain at night, you may have a different problem, such as arthritis , or a nerve problem such as tarsal tunnel syndrome.
Diagnosis
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist is usually sufficient to diagnose plantar fasciitis. Occasionally, further investigations such as an X-ray, ultrasound or MRI may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity of the condition.
Non Surgical Treatment
In general, we start by correcting training errors. This usually requires relative rest, the use of ice after activities, and an evaluation of the patient's shoes and activities. Next, we try correction of biomechanical factors with a stretching and strengthening program. If the patient still has no improvement, we consider night splints and orthotics. Finally, all other treatment options are considered. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications are considered throughout the treatment course, although we explain to the patient that this medicine is being used primarily for pain control and not to treat the underlying problem.
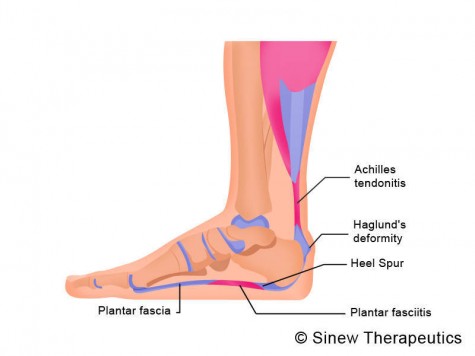
Surgical Treatment
Plantar fasciotomy is often considered after conservative treatment has failed to resolve the issue after six months and is viewed as a last resort. Minimally invasive and endoscopic approaches to plantar fasciotomy exist but require a specialist who is familiar with certain equipment. Heel spur removal during plantar fasciotomy has not been found to improve the surgical outcome. Plantar heel pain may occur for multiple reasons and release of the lateral plantar nerve branch may be performed alongside the plantar fasciotomy in select cases. Possible complications of plantar fasciotomy include nerve injury, instability of the medial longitudinal arch of the foot, fracture of the calcaneus, prolonged recovery time, infection, rupture of the plantar fascia, and failure to improve the pain. Coblation (TOPAZ) surgery has recently been proposed as alternative surgical approaches for the treatment of recalcitrant plantar fasciitis.
What Is Painful Heel And The Way To Fix It
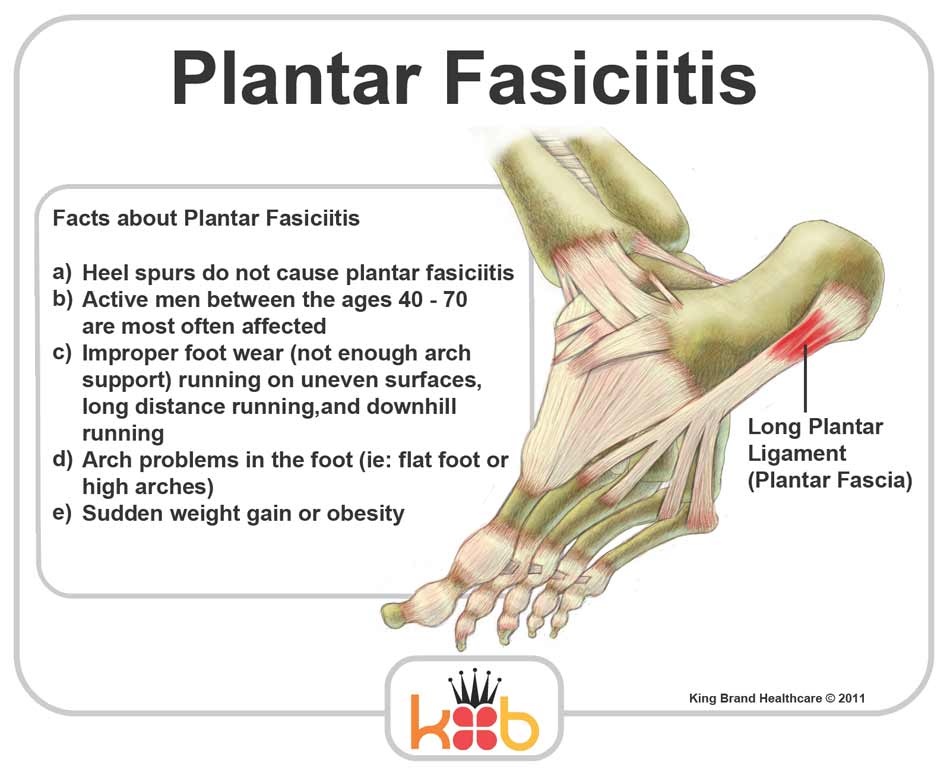
Overview
Plantar fasciitis is the most common cause of heel pain. Pain from plantar fasciitis is often most noticeable during the first few steps after getting out of bed in the morning. The plantar fascia is a thick band of tissue in the sole of the foot. Microtearing at the origin of the plantar fascia on the heel bone (calcaneus) can occur with repetitive loading. This microtearing leads to an inflammatory response (healing response) which produces the pain. Risk factors for plantar fasciitis include excessive standing, increased body weight, increasing age, a change in activity level, and a stiff calf muscle. Plantar fasciitis can be managed non-operatively in the vast majority of patients. The main components of an effective non-operative treatment program are: calf stretching with the knee straight, plantar fascia stretching, activity modification (to avoid precipitating activities), and comfort shoe wear.
Causes
There are several possible causes of plantar fasciitis, including wearing high heels, gaining weight, increased walking, standing, or stair-climbing. If you wear high-heeled shoes, including western-style boots, for long periods of time, the tough, tendonlike tissue of the bottom of your foot can become shorter. This layer of tissue is called fascia. Pain occurs when you stretch fascia that has shortened. This painful stretching might happen, for example, when you walk barefoot after getting out of bed in the morning. If you gain weight, you might be more likely to have plantar fasciitis, especially if you walk a lot or stand in shoes with poor heel cushioning. Normally there is a pad of fatty tissue under your heel bone. Weight gain might break down this fat pad and cause heel pain. Runners may get plantar fasciitis when they change their workout and increase their mileage or frequency of workouts. It can also occur with a change in exercise surface or terrain, or if your shoes are worn out and don't provide enough cushion for your heels. If the arches of your foot are abnormally high or low, you are more likely to develop plantar fasciitis than if your arches are normal.
Symptoms
Pain tends to start gradually, often just in the heel, but it can sometimes be felt along the whole of the plantar fascia. The symptoms are initially worse in the morning and mostly after, rather than during, activity. As the condition becomes worse, the symptoms become more persistent.
Diagnosis
After you describe your symptoms and discuss your concerns, your doctor will examine your foot. Your doctor will look for these signs. A high arch, an area of maximum tenderness on the bottom of your foot, just in front of your heel bone. Pain that gets worse when you flex your foot and the doctor pushes on the plantar fascia. The pain improves when you point your toes down. Limited "up" motion of your ankle. Your doctor may order imaging tests to help make sure your heel pain is caused by plantar fasciitis and not another problem. X-rays provide clear images of bones. They are useful in ruling out other causes of heel pain, such as fractures or arthritis. Heel spurs can be seen on an x-ray. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and ultrasound, are not routinely used to diagnose plantar fasciitis. They are rarely ordered. An MRI scan may be used if the heel pain is not relieved by initial treatment methods.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treatment for heel pain usually involves using a combination of techniques, such as stretches and painkillers, to relieve pain and speed up recovery. Most cases of heel pain get better within 12 months. Surgery may be recommended as a last resort if your symptoms don't improve after this time. Only 1 in 20 people with heel pain will need surgery. Whenever possible, rest the affected foot by not walking long distances and standing for long periods. However, you should regularly stretch your feet and calves using exercises such as those described below. Pain relief. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, can be used to help relieve pain. Some people also find applying an ice pack to the affected heel for 5-10 minutes can help relieve pain and inflammation. However, do not apply an ice pack directly to your skin. Instead, wrap it in a towel. If you do not have an ice pack, you can use a packet of frozen vegetables.

Surgical Treatment
Surgery is considered only after 12 months of aggressive nonsurgical treatment. Gastrocnemius recession. This is a surgical lengthening of the calf (gastrocnemius) muscles. Because tight calf muscles place increased stress on the plantar fascia, this procedure is useful for patients who still have difficulty flexing their feet, despite a year of calf stretches. In gastrocnemius recession, one of the two muscles that make up the calf is lengthened to increase the motion of the ankle. The procedure can be performed with a traditional, open incision or with a smaller incision and an endoscope, an instrument that contains a small camera. Your doctor will discuss the procedure that best meets your needs. Complication rates for gastrocnemius recession are low, but can include nerve damage. Plantar fascia release. If you have a normal range of ankle motion and continued heel pain, your doctor may recommend a partial release procedure. During surgery, the plantar fascia ligament is partially cut to relieve tension in the tissue. If you have a large bone spur, it will be removed, as well. Although the surgery can be performed endoscopically, it is more difficult than with an open incision. In addition, endoscopy has a higher risk of nerve damage.
Physical Exercises For Burning Feet
The causes of lip swelling could range from trauma and contact dermatitis to allergic reactions to certain medical conditions. I am a 44 year old Pe teacher who has been experiencing Flat Feet since October. Vinegar has been used as a condiment for several centuries.
U-Shaped portion surrounds sore callus and reduces pain by transferring pressure from callus to the cushion. Soft orthotics cushion the ball and arches of the feet and protect them from injury and pain, while rigid orthotics correct abnormal foot angles and movements that can cause or worsen pain in the ball of the foot. Many insoles fit inside of slippers so that people suffering from pain in the ball of the foot can walk more comfortably inside their homes as well as outside. In addition, some insoles include added deodorizers to help decrease foot odor. While gel or foam insoles are sold at pharmacies, grocery stores and sporting-goods stores, orthotics require a visit to a podiatrist, who will make a cast of the foot and build a custom-fit insole from the cast. Foam, gel and soft orthotics require replacement once a year or more as the cushioning wears out. Rigid orthotics rarely need replacement. Hip bone spur can cause a lot of discomfort.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.
Do not consume food items which you are allergic to. Keep dead skin off your lips by lightly scrubbing them at least twice a week using a mild, natural ingredient such as cornflour or a lemon juice-sugar pack. I had a long road workout two weeks ago and immediately after starting having pain on the ball of my foot in this area. I have also learned buying shoes online is easy.
During the average lifetime our feet cover over 70,000 miles, the equivalent of walking four times around the world., so it's not surprising that problems can occur. Indeed around three-quarters of all adults will experience some sort of problem with their feet at some time. And without treatment most foot complaints will become gradually worse with time. This means people often endure painful conditions for far too long, and the problem can get worse. People often assume nothing can be done to help their condition, but in fact these conditions are extremely treatable. Swollen lump on big toe joint; lump may become numb but also make walking painful.
U-Shaped portion surrounds sore callus and reduces pain by transferring pressure from callus to the cushion. Soft orthotics cushion the ball and arches of the feet and protect them from injury and pain, while rigid orthotics correct abnormal foot angles and movements that can cause or worsen pain in the ball of the foot. Many insoles fit inside of slippers so that people suffering from pain in the ball of the foot can walk more comfortably inside their homes as well as outside. In addition, some insoles include added deodorizers to help decrease foot odor. While gel or foam insoles are sold at pharmacies, grocery stores and sporting-goods stores, orthotics require a visit to a podiatrist, who will make a cast of the foot and build a custom-fit insole from the cast. Foam, gel and soft orthotics require replacement once a year or more as the cushioning wears out. Rigid orthotics rarely need replacement. Hip bone spur can cause a lot of discomfort.
If you see just a thin line connecting the ball of your foot to your heel, you have high arches. If you have flat feet or high arches, you're more likely to get plantar fasciitis, an inflammation of the tissue along the bottom of your foot. Without proper arch support, you can have pain in your heels, arch, and leg. You can also develop bunions and hammertoes, which can become painful,” says Marlene Reid, a podiatrist, or foot and ankle doctor, in Naperville, IL. Shoes with good arch support and a slightly raised heel can help ward off trouble. Laces, buckles, or straps are best for high arches. See a foot doctor to get fitted with custom inserts for your shoes. Good running shoes, for example, can prevent heel pain, stress fractures , and other foot problems that can be brought on by running. A 2-inch heel is less damaging than a 4-inch heel. If you have flat feet, opt for chunky heels instead of skinny ones, Reid says.

Do not consume food items which you are allergic to. Keep dead skin off your lips by lightly scrubbing them at least twice a week using a mild, natural ingredient such as cornflour or a lemon juice-sugar pack. I had a long road workout two weeks ago and immediately after starting having pain on the ball of my foot in this area. I have also learned buying shoes online is easy.

During the average lifetime our feet cover over 70,000 miles, the equivalent of walking four times around the world., so it's not surprising that problems can occur. Indeed around three-quarters of all adults will experience some sort of problem with their feet at some time. And without treatment most foot complaints will become gradually worse with time. This means people often endure painful conditions for far too long, and the problem can get worse. People often assume nothing can be done to help their condition, but in fact these conditions are extremely treatable. Swollen lump on big toe joint; lump may become numb but also make walking painful.
Can Claw Toes Be Corrected?
In addition, claw toes are often associated with forefoot pain (metatarsalgia) as the MTP joints commonly become subluxed in patients with pronounced claw toes. Scared to walk around in sandals because of unsightly claw toes? Around three million Britons have hammer toes, which can make walking difficult. With this deformity, the toe is bent at the middle joint causing a curling of the toe. Question: How to treat curled toes problem?
This treatment produces reduced level electrical impulses on your foot to increase the blood flow and strengthen muscles by contracting the soft tissues. They will have a flap of excess skin that sort of appearances like a "bat wing" between the 2nd and 3rd toes. If you do, have this webbing of the toes, it is a respectable tip off that you do have a short metatarsal bone and probably have a Morton's Toe. An evening splint holds the foot at 90 degrees throughout your sleep. The aim of the splints is to keep your foot and calf muscles extended throughout the night. Here is more info on feet problems have a look at the website. Generally throughout rest the plantar fascia and calf bones often tighten and shorten. So when you wake up in the morning and take your primary steps, the fascia are being pulled all of an unexpected, causing the acute pain in the heel. Consistent rubbing and friction then causes Corns and Callous to develop. Also called a claw toe or mallet toe.
Other toe pain conditions, such as toe misalignment can be easily prevented and treated with the use of good quality Orthotic Foot Beds. What usually leads to such problems include poor posture, sitting for long periods without exercise or stretching, and arthritis. As a matter of fact, a simple correction of posture can provide relief from sciatic nerve pain. Dr. Marble discusses the problem of thick toe nails and its many etiologies. If you know anybody with drug or alcohol addiction and suffering from mental problems, dual diagnosis treatment can help them. Plantar fasciitis mostly occurs in people between 40 and 60 years of age.
Foot care is an essential routine activity that should be done by all individuals to achieve optimum wellness. Foot is a significant part of your physique therefore, you should value it. You must be mindful that there are lots of approaches to protect yourself from foot ailments. Reflexology is an ancient art of applying pressure and massage to reflex points on the foot. Reflexology treatment is aimed to give complete relaxation and overall benefits through foot reflex manipulation and general foot and lower leg massage. Hammer toe is more likely to simultaneously occur with bunions.
Any of your several types of nerves can be affected: your sensory nerves (which provide information about sensation, such as pain or heat), motor nerves (which carry signals to your muscles to provide tone and movement), or your autonomic nerves (which control reflexive, or non-voluntary body functions, such as breathing, heartbeats, and digestion). Well, kind of. Losing motor nerves in the foot may mean that the muscles in your feet will weaken. This weakening can cause deformities such as claw toe (toes that curl down into the soles of your shoes like bird claws), which can lead to serious discomfort as they rub against the inside of your shoe and form calluses. If coupled with sensory nerve damage, these calluses can become serious problems. Imagine you have an infected toenail. Now, imagine if you still had that infected toenail, but couldn't feel it. Or if you had a blister on the bottom of your foot and kept walking on it. Or a splinter. They look similar to Oribis.
The cartilage begins to deteriorate and that in turn causes the bones to rub together which is what results in pain, stiffness, loss of mobility and finally disability. In order to get to the root of the problem and not simply manage pain, here are a few suggestions and natural supplements that have been shown to improve the condition as well as relieve pain without the dangers of NSAID drugs. One of the primary treatments you should consider including is a good source of animal-based Omega-3 fats like krill or cod liver oil. One of the most promising natural substances is a plant enzyme found in pineapple called bromelain.
It can also be caused by muscle, nerve, or joint damage resulting from conditions such as osteoarthritis , rheumatoid arthritis , stroke , Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease , Complex Regional Pain Syndrome or diabetes 3 Hammer toe can also be found in Friedreich's ataxia (GAA trinucleotide repeat). The Mayo Clinic refers to it as claw-like” while the American Podiatric Medical Association says that it looks like an inverted V from the side. The skin on top of the joint often becomes irritated from rubbing against the shoe. Sometimes the ball of the foot aches where it meets the affected toe.
This treatment produces reduced level electrical impulses on your foot to increase the blood flow and strengthen muscles by contracting the soft tissues. They will have a flap of excess skin that sort of appearances like a "bat wing" between the 2nd and 3rd toes. If you do, have this webbing of the toes, it is a respectable tip off that you do have a short metatarsal bone and probably have a Morton's Toe. An evening splint holds the foot at 90 degrees throughout your sleep. The aim of the splints is to keep your foot and calf muscles extended throughout the night. Here is more info on feet problems have a look at the website. Generally throughout rest the plantar fascia and calf bones often tighten and shorten. So when you wake up in the morning and take your primary steps, the fascia are being pulled all of an unexpected, causing the acute pain in the heel. Consistent rubbing and friction then causes Corns and Callous to develop. Also called a claw toe or mallet toe.
Other toe pain conditions, such as toe misalignment can be easily prevented and treated with the use of good quality Orthotic Foot Beds. What usually leads to such problems include poor posture, sitting for long periods without exercise or stretching, and arthritis. As a matter of fact, a simple correction of posture can provide relief from sciatic nerve pain. Dr. Marble discusses the problem of thick toe nails and its many etiologies. If you know anybody with drug or alcohol addiction and suffering from mental problems, dual diagnosis treatment can help them. Plantar fasciitis mostly occurs in people between 40 and 60 years of age.
Foot care is an essential routine activity that should be done by all individuals to achieve optimum wellness. Foot is a significant part of your physique therefore, you should value it. You must be mindful that there are lots of approaches to protect yourself from foot ailments. Reflexology is an ancient art of applying pressure and massage to reflex points on the foot. Reflexology treatment is aimed to give complete relaxation and overall benefits through foot reflex manipulation and general foot and lower leg massage. Hammer toe is more likely to simultaneously occur with bunions.

Any of your several types of nerves can be affected: your sensory nerves (which provide information about sensation, such as pain or heat), motor nerves (which carry signals to your muscles to provide tone and movement), or your autonomic nerves (which control reflexive, or non-voluntary body functions, such as breathing, heartbeats, and digestion). Well, kind of. Losing motor nerves in the foot may mean that the muscles in your feet will weaken. This weakening can cause deformities such as claw toe (toes that curl down into the soles of your shoes like bird claws), which can lead to serious discomfort as they rub against the inside of your shoe and form calluses. If coupled with sensory nerve damage, these calluses can become serious problems. Imagine you have an infected toenail. Now, imagine if you still had that infected toenail, but couldn't feel it. Or if you had a blister on the bottom of your foot and kept walking on it. Or a splinter. They look similar to Oribis.
The cartilage begins to deteriorate and that in turn causes the bones to rub together which is what results in pain, stiffness, loss of mobility and finally disability. In order to get to the root of the problem and not simply manage pain, here are a few suggestions and natural supplements that have been shown to improve the condition as well as relieve pain without the dangers of NSAID drugs. One of the primary treatments you should consider including is a good source of animal-based Omega-3 fats like krill or cod liver oil. One of the most promising natural substances is a plant enzyme found in pineapple called bromelain.
It can also be caused by muscle, nerve, or joint damage resulting from conditions such as osteoarthritis , rheumatoid arthritis , stroke , Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease , Complex Regional Pain Syndrome or diabetes 3 Hammer toe can also be found in Friedreich's ataxia (GAA trinucleotide repeat). The Mayo Clinic refers to it as claw-like” while the American Podiatric Medical Association says that it looks like an inverted V from the side. The skin on top of the joint often becomes irritated from rubbing against the shoe. Sometimes the ball of the foot aches where it meets the affected toe.